SQL Server FAQ With Answer , Must Read To all SQL-Server User:
JOIN:
A Join is used for displaying columns with the
same or different names from different tables. The output displayed will have
all the columns shown individually. i.e. The columns will be aligned next to
each other.
By using join, you can retrieve data from two or more tables based on logical relationships between the tables. Joins indicate how sql should use data from one table to select the rows in another table.
UNION:
The UNION set operator is used for combining
data from two tables which have columns with the same datatype. When a UNION is
performed the data from both tables will be collected in a single column having
the same datatype.
Union combines the unique results of two or more queries into a single result set that includes all the rows that belong to all queries in the union.
For Sql-2008:
Deadlock:A common issue with SQL Server is deadlocks. A deadlock occurs when two or more processes are waiting on the same resource and each process is waiting on the other process to complete before moving forward. When this situation occurs and there is no way for these processes to resolve the conflict, SQL Server will choose one of processes as the deadlock victim and rollback that process, so the other process or processes can move forward.
Blocking
Blocking occurs when one connection (user process or application process) places a lock on a table or a number of rows and a second connection attempts to read or modify the data under the lock by first connection. Depending on the type of the lock, this can cause the second connection to wait until the first connection releases its lock. A blocked connection waits indefinitely for the blocking connection to release its lock.
The more blocking happens on the server the less concurrency the system achieves. A certain amount of blocking is unavoidable but too many blocks for longer periods of time can degrade the performance of SQL Server.
Livelock:A Live lock is one, where a request for exclusive lock is denied continuously because a series of overlapping shared locks keeps on interfering each other and to adapt from each other they keep on changing the status which further prevents them to complete the task. In SQL Server Live Lock occurs when read transactions are applied on table which prevents write transaction to wait indefinitely. This is different then deadlock as in deadlock both the processes wait on each other.
Different types of normalization in SQL-SERVER?
DE- NORMALIZATION:
Denormalization is the process of adding redundant data to speed up complex queries involving multiple table JOINS. One might just go to a lower form of Normalization to achieve Denormalization and better performance. Data is included in one table from another in order to eliminate the second table which reduces the number of JOINS in a query and thus achieves performance.
Normalization is a Six stage process - After the first stage, the data is said to be in first normal form, after the second, it is in second normal form, after the third, it is in third normal form and so on.
Definition: An entity is in the first normal form if it contains no repeating groups. In relational terms, a table is in the first normal form if it contains no repeating columns. Repeating columns make your data less flexible, waste disk space, and make it more difficult to search for data.
IMP: In 1NF relation the order of tuples (rows) and attributes (columns) does not matter.
Example:
The above relation satisfies the properties of a relation and is said to be in first normal form (or 1NF). Conceptually it is convenient to have all the information in one relation since it is then likely to be easier to query the database.
Second Normal Form (2nd NF)
In 2nd NF:
Definition: A relation is in 2NF if it is in 1NF and every non-key attribute is fully dependent on each candidate key of the relation.
Example:
The following relation is not in Second Normal Form:
In the table above, the order number serves as the primary key. Notice that the customer and total amount are dependent upon the order number -- this data is specific to each order. However, the contact person is dependent upon the customer. An alternative way to accomplish this would be to create two tables:
The creation of two separate tables eliminates the dependency problem. In the first table, contact person is dependent upon the primary key -- customer name. The second table only includes the information unique to each order. Someone interested in the contact person for each order could obtain this information by performing a Join Operation.
Third Normal Form (3rd NF)
In 3rd NF:
A relation is in third normal form, if it is in 2NF and every non-key attribute of the relation is non-transitively dependent on each candidate key of the relation.
Non-transitive dependency:
Let A, B and C be three attributes of a relation R such that Aïƒ B and Bïƒ C. From these FDs, we may derive Aïƒ C. This dependence Aïƒ C is transitive.
Example:
The above table is not in the 3NF.
In this example, the city and state are dependent upon the ZIP code. To place this table in 3NF, two separate tables would be created -- one containing the company name and ZIP code and the other containing city, state, ZIP code pairings.
This may seem overly complex for daily applications and indeed it may be. Database designers should always keep in mind the tradeoffs between higher level normal forms and the resource issues that complexity creates.
Boyce-Codd Normal Form (BCNF)
In BCNF:
Definition: A relation is in Boyce-Codd Normal Form (BCNF) if every determinant is a candidate key. (See the links in the box at right for definitions of determinant and candidate key.)
The difference between 3NF and BCNF is that for a functional dependency A ïƒ B, 3NF allows this dependency in a relation if B is a primary-key attribute and A is not a candidate key,
Whereas BCNF insists that for this dependency to remain in a relation, A must be a candidate key.
Example:
CLIENT INTERVIEW:
• FD1 ClientNo, InterviewDate -> InterviewTime, StaffNo, RoomNo (Primary Key)
• FD2 StaffNo, InterviewDate, InterviewTime -> ClientNo (Candidate key)
• FD3 RoomNo, InterviewDate, InterviewTime -> ClientNo, StaffNo (Candidate key)
• FD4 StaffNo, InterviewDate -> RoomNo (not a candidate key)
As a consequece the ClientInterview relation may suffer from update anomalies.
To transform the ClientInterview relation to BCNF, we must remove the violating functional dependency by creating two new relations called Interview and StaffRoom as shown below,
Interview (ClientNo, InterviewDate, InterviewTime, StaffNo)
StaffRoom (StaffNo, InterviewDate, RoomNo)
INTERVIEW
STAFFROOM
BCNF Interview and StaffRoom relations.
An entity is in Fourth Normal Form (4NF) when it meets the requirement of being in Third Normal Form (3NF) and additionally:
Fourth Normal Form (4th NF)
In 4th NF:
An entity is in Fourth Normal Form (4NF) when it meets the requirement of being in Third Normal Form (3NF) and additionally:
In relational databases, many-to-many relationships are expressed through cross-reference tables.
Definition: A table is in fourth normal form (4NF) if and only if it is in BCNF and contains no more than one multi-valued dependency.
Example:
Take an example of Employee Table
info(Employee, Skills, Hobbies)
This table is difficult to maintain since adding a new hobby requires multiple new rows corresponding to each skill. This problem is created by the pair of multi-valued dependencies EMPLOYEE -> SKILLS and EMPLOYEE -> HOBBIES. A much better alternative would be to decompose INFO into two relations:
Hobbies(Employee, Hobby)
Fifth Normal Form (5th NF)
In 5th NF:
Definition: A table is in fifth normal form (5NF) or Project-Join Normal Form (PJNF) if it is in 4NF and it cannot have a lossless decomposition into any number of smaller tables.
Fifth normal form, also known as join-projection normal form (JPNF), states that no non-trivial join dependencies exist. 5NF states that any fact should be able to be reconstructed without any anomalous results in any case, regardless of the number of tables being joined. A 5NF table should have only candidate keys and it's primary key should consist of only a single column.
Example:
Take an example of a buying table. This is used to track buyers, what they buy, and from whom they buy. Take the following sample data:
The problem with the above table structure is that if Claiborne starts to sell Jeans then how many records must you create to record this fact? The problem is there are pair wise cyclical dependencies in the primary key. That is, in order to determine the item you must know the buyer and vendor, and to determine the vendor you must know the buyer and the item, and finally to know the buyer you must know the vendor and the item.
And the solution is to break this one table into three tables; Buyer-Vendor, Buyer-Item, and Vendor-Item. So following tables are in the 5NF.
BUYER-VENDOR
VENDOR- ITEM
Difference between correlated subquery and nested subquery :-
Subquery:-If a sql statement contains another sql statement then the sql statement which is inside another sql statement is called Subquery. It is also known as nested query. The Sql Statement which contains the other sql statement is called Parent Statement.
Nested Subquery:-If a Subquery contains another subquery, then the subquery inside another subquery is called nested subquery.
Correlated Subquery
A query is called correlated subquery when
both the inner query and the outer query are interdependent. For every row
processed by the inner query, the outer query is processed as well. The inner
query depends on the outer query before it can be processed.
what
is database transaction? properties of transaction?
what is computed column in sql server:-
What is Linked Servers or
Database Links?How to setup Linked Servers?
select max(salary) from Employeedetails
where salary not in (select top 1 salary from Employeedetails order by salary desc )
3nd Highest Salary
select max(salary) from Employeedetails
where salary not in (select top 2 salary from Employeedetails order by salary desc )
4nd Highest Salary
select max(salary) from Employeedetails
where salary not in (select top 3 salary from Employeedetails order by salary desc )
...................
Both Having Clause and Where clause is used
to filter the data coming from the Select statement, but still there are some
differences between them. These difference are given below
1) Where clause can
be used with Select, Update and Delete Statement Clause but having clause can
be used only with Select statement.
For example, the
sql query
Update EmployeeDeptInfo Set departmentid =7 Where
employeeid=4
will work fine but the
query
Update EmployeeDeptInfo Set departmentid =7 Having
employeeid=4
will not work
2) We can't use
aggregate functions in the where clause unless it is in a subquery contained in
a HAVING clause whereas we can use aggregate function in Having clause.
We can use column name in Having clause but the column must be contained in the
group by clause.
For example,
the sql query
select *
from EmployeeDeptInfo where count(employeeid)>1
will
not work but the query
Select
Employeeid, Departmentid from EmployeeDeptInfo Group By Employeeid,
DepartmentId having (count(employeeid) >1)
will work fine
3) Where Clause is
used on the individual records whereas Having Clause in conjunction with Group
By Clause work on the record sets ( group of records ).
For Example, in the
below sql Query
select employeeid, departmentid from EmployeeDeptInfo where
employeeid=5
the where clause
will search the table EmployeeDeptInfo for the record whose employeeid is
5 and then show the output.
but in the below
query,
Select
Employeeid, Departmentid from EmployeeDeptInfo Group By Employeeid,
DepartmentId having employeeid=5
the result
are first grouped by the Group By Clause and then they become again
filtered by the condition defined in the having clause. Sometime , like above
both queries, we get the same result with the help of Where clause and having
clause but which way is best is determined automatically by the optimizer and
it select the best way of executing it.
Where Clause:
1.Where Clause can be used other than Select statement also
2.Where applies to each and single row
3.In where clause the data that fetched from memory according
to condition
4.Where is used before GROUP BY clause
Ex:Using Condition for the data in the memory.
Having Clause:
1.Having is used only with the SELECT statement.
2.Having applies to summarized rows (summarized with GROUP BY)
3.In having the completed data firstly fetched and then separated according to condition.
4.HAVING clause is used to impose condition on GROUP Function and is used after GROUP BY clause in the query
Ex: when using the avg function and then filter the data like ava(Sales)>0
Summary:
Having works like Where clause with out Group By Clause
1.Where Clause can be used other than Select statement also
2.Where applies to each and single row
3.In where clause the data that fetched from memory according
to condition
4.Where is used before GROUP BY clause
Ex:Using Condition for the data in the memory.
Having Clause:
1.Having is used only with the SELECT statement.
2.Having applies to summarized rows (summarized with GROUP BY)
3.In having the completed data firstly fetched and then separated according to condition.
4.HAVING clause is used to impose condition on GROUP Function and is used after GROUP BY clause in the query
Ex: when using the avg function and then filter the data like ava(Sales)>0
Summary:
Having works like Where clause with out Group By Clause
Difference between join and union?
JOIN:
A Join is used for displaying columns with the
same or different names from different tables. The output displayed will have
all the columns shown individually. i.e. The columns will be aligned next to
each other.By using join, you can retrieve data from two or more tables based on logical relationships between the tables. Joins indicate how sql should use data from one table to select the rows in another table.
UNION:
The UNION set operator is used for combining
data from two tables which have columns with the same datatype. When a UNION is
performed the data from both tables will be collected in a single column having
the same datatype.Union combines the unique results of two or more queries into a single result set that includes all the rows that belong to all queries in the union.
Difference between cross product
and cartesian product?
There is no difference. Cartesian Products and Cross Joins are the
same.
Retrieve data 11th column of the
nth column
select 1/2 in sql server.What
is Result
zero (0)
difference between inner join and
outer join
Inner Join
The join that
displays only the rows that have a match in both the joined tables is known as
inner join. This is default join in the query and view Designer.
Outer Joins
A join that return
all the rows that satisfy the condition and unmatched rows in the joined table
is an Outer Join.
We are having three
types of Outer Joins
Left Outer Join
Right Outer Join
Full Outer Join
Left Outer Join
The left outer join
displays all the rows from the first table and matched rows from the second
table.
Right Outer Join
The right outer
join displays all the rows from the second table and matched rows from the
first table.
Full Outer Join
Full Outer Join
displays all the matching and non matching rows of both the tables.
What is Index?Types of
Indexes .How Many Clustered Indexes
Can be created on
a table .i created a separate
index on each column of a table.what are the advantages and disadvantages of
this approach
An index can be created
in a table to increase the performance of application and we can get the data
more quickly and efficiently.
In SQL we are having two types of indexes are there
1) Clustered Index
2) Non-Clustered Index
Clustered Index
A clustered index is a special type of index that reorders the way
records in the table are physically stored. Therefore table can have only one
clustered index. The leaf nodes of a clustered index contain the data pages.
Non-Clustered Index
A
non-clustered index is a special type of index in which the logical order of
the index does not match the physical stored order of the rows on disk. The
leaf node of a non-clustered index does not consist of the data pages. Instead,
the leaf nodes contain index rows.
Maximum number
of Index per
table.
For Sql-2005:
1ClusteredIndex+249NonclusteredIndex=250Index
For Sql-2008:
1ClusteredIndex+999NonclusteredIndex=1000Index
If you create an index on
each column of a table, it improves the query (i.e. SELECT) performance, as the
query optimizer can choose from all the existing indexes to come up with an
efficient execution plan. At the same time, data modification operations (such
as INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE) will become slow, as every time data changes in
the table, all the indexes need to be updated. Another disadvantage is that,
indexes need disk space, the more indexes you have, more disk space is used.
What is a deadlock,Blocking and what
is a live lock? Deadlock:A common issue with SQL Server is deadlocks. A deadlock occurs when two or more processes are waiting on the same resource and each process is waiting on the other process to complete before moving forward. When this situation occurs and there is no way for these processes to resolve the conflict, SQL Server will choose one of processes as the deadlock victim and rollback that process, so the other process or processes can move forward.
Blocking
Blocking occurs when one connection (user process or application process) places a lock on a table or a number of rows and a second connection attempts to read or modify the data under the lock by first connection. Depending on the type of the lock, this can cause the second connection to wait until the first connection releases its lock. A blocked connection waits indefinitely for the blocking connection to release its lock.
The more blocking happens on the server the less concurrency the system achieves. A certain amount of blocking is unavoidable but too many blocks for longer periods of time can degrade the performance of SQL Server.
Livelock:A Live lock is one, where a request for exclusive lock is denied continuously because a series of overlapping shared locks keeps on interfering each other and to adapt from each other they keep on changing the status which further prevents them to complete the task. In SQL Server Live Lock occurs when read transactions are applied on table which prevents write transaction to wait indefinitely. This is different then deadlock as in deadlock both the processes wait on each other.
Different types of normalization in SQL-SERVER?
NORMALIZATION:
Normalization is the process of organizing data into a related table; it also eliminates redundancy and increases the integrity which improves performance of the query. To normalize a database, we divide the database into tables and establish relationships between the tables.
Database normalization can essentially be defined as the practice of optimizing table structures. Optimization is accomplished as a result of a thorough investigation of the various pieces of data that will be stored within the database, in particular concentrating upon how this data is interrelated.
Normalization Avoids:
Normalization is the process of organizing data into a related table; it also eliminates redundancy and increases the integrity which improves performance of the query. To normalize a database, we divide the database into tables and establish relationships between the tables.
Database normalization can essentially be defined as the practice of optimizing table structures. Optimization is accomplished as a result of a thorough investigation of the various pieces of data that will be stored within the database, in particular concentrating upon how this data is interrelated.
Normalization Avoids:
- Duplication of Data -
The same data is listed in multiple lines of the database
- Insert Anomaly - A record about an entity
cannot be inserted into the table without first inserting information
about another entity - Cannot enter a customer without a sales order
- Delete Anomaly - A record cannot be
deleted without deleting a record about a related entity. Cannot delete a
sales order without deleting all of the customer's information.
- Update Anomaly - Cannot update information
without changing information in many places. To update customer
information, it must be updated for each sales order the customer has
placed
DE- NORMALIZATION:
Denormalization is the process of adding redundant data to speed up complex queries involving multiple table JOINS. One might just go to a lower form of Normalization to achieve Denormalization and better performance. Data is included in one table from another in order to eliminate the second table which reduces the number of JOINS in a query and thus achieves performance.
Normalization is a Six stage process - After the first stage, the data is said to be in first normal form, after the second, it is in second normal form, after the third, it is in third normal form and so on.
First Normal Form
(1st NF)
In 1st NF:
In 1st NF:
- The
table cells must be of single value.
- Eliminate
repeating groups in individual tables.
- Create
a separate table for each set of related data.
- Identify
each set of related data with a primary key.
Definition: An entity is in the first normal form if it contains no repeating groups. In relational terms, a table is in the first normal form if it contains no repeating columns. Repeating columns make your data less flexible, waste disk space, and make it more difficult to search for data.
IMP: In 1NF relation the order of tuples (rows) and attributes (columns) does not matter.
Example:
Order
|
Customer
|
Contact Person
|
Total
|
1
|
Rishabh
|
Manish
|
134.23
|
2
|
Preeti
|
Rohan
|
521.24
|
3
|
Rishabh
|
Manish
|
1042.42
|
4
|
Rishabh
|
Manish
|
928.53
|
The above relation satisfies the properties of a relation and is said to be in first normal form (or 1NF). Conceptually it is convenient to have all the information in one relation since it is then likely to be easier to query the database.
Second Normal Form (2nd NF)
In 2nd NF:
- Remove
Partial Dependencies.
- Functional
Dependency: The value of one attribute in a table is determined entirely
by the value of another.
- Partial
Dependency: A type of functional dependency where an attribute is
functionally dependent on only part of the primary key (primary key must
be a composite key).
- Create
separate table with the functionally dependent data and the part of the
key on which it depends. Tables created at this step will usually contain
descriptions of resources.
Definition: A relation is in 2NF if it is in 1NF and every non-key attribute is fully dependent on each candidate key of the relation.
Example:
The following relation is not in Second Normal Form:
Order
|
Customer
|
Contact Person
|
Total
|
1
|
Rishabh
|
Manish
|
134.23
|
2
|
Preeti
|
Rohan
|
521.24
|
3
|
Rishabh
|
Manish
|
1042.42
|
4
|
Rishabh
|
Manish
|
928.53
|
In the table above, the order number serves as the primary key. Notice that the customer and total amount are dependent upon the order number -- this data is specific to each order. However, the contact person is dependent upon the customer. An alternative way to accomplish this would be to create two tables:
Customer
|
Contact Person
|
Rishabh
|
Manish
|
Preeti
|
Rohan
|
Order
|
Customer
|
Total
|
1
|
Rishabh
|
134.23
|
2
|
Preeti
|
521.24
|
3
|
Rishabh
|
1042.42
|
4
|
Rishabh
|
928.53
|
The creation of two separate tables eliminates the dependency problem. In the first table, contact person is dependent upon the primary key -- customer name. The second table only includes the information unique to each order. Someone interested in the contact person for each order could obtain this information by performing a Join Operation.
Third Normal Form (3rd NF)
In 3rd NF:
- Remove
transitive dependencies.
- Transitive
Dependency A type of functional dependency where an attribute is
functionally dependent on an attribute other than the primary key. Thus
its value is only indirectly determined by the primary key.
- Create
a separate table containing the attribute and the fields that are
functionally dependent on it. Tables created at this step will usually
contain descriptions of either resources or agents. Keep a copy of the key
attribute in the original file.
A relation is in third normal form, if it is in 2NF and every non-key attribute of the relation is non-transitively dependent on each candidate key of the relation.
Non-transitive dependency:
Let A, B and C be three attributes of a relation R such that Aïƒ B and Bïƒ C. From these FDs, we may derive Aïƒ C. This dependence Aïƒ C is transitive.
Example:
Company
|
City
|
State
|
ZIP
|
ABC Ltd.
|
Mumbai
|
MH
|
10169
|
XYZ Ltd.
|
Noida
|
UP
|
33196
|
ASD Ltd.
|
Chennai
|
TN
|
21046
|
The above table is not in the 3NF.
In this example, the city and state are dependent upon the ZIP code. To place this table in 3NF, two separate tables would be created -- one containing the company name and ZIP code and the other containing city, state, ZIP code pairings.
Company
|
ZIP
|
ABC Ltd.
|
10169
|
XYZ Ltd.
|
33196
|
ASD Ltd.
|
21046
|
City
|
State
|
ZIP
|
Mumbai
|
MH
|
10169
|
Noida
|
UP
|
33196
|
Chennai
|
TN
|
21046
|
This may seem overly complex for daily applications and indeed it may be. Database designers should always keep in mind the tradeoffs between higher level normal forms and the resource issues that complexity creates.
Boyce-Codd Normal Form (BCNF)
In BCNF:
- When a
relation has more than one candidate key, anomalies may result even though
the relation is in 3NF.
- 3NF
does not deal satisfactorily with the case of a relation with overlapping
candidate keys
- i.e.
composite candidate keys with at least one attribute in common.
- BCNF
is based on the concept of a determinant.
- A
determinant is any attribute (simple or composite) on which some other
attribute is fully functionally dependent.
- A
relation is in BCNF is, and only if, every determinant is a candidate key.
Definition: A relation is in Boyce-Codd Normal Form (BCNF) if every determinant is a candidate key. (See the links in the box at right for definitions of determinant and candidate key.)
The difference between 3NF and BCNF is that for a functional dependency A ïƒ B, 3NF allows this dependency in a relation if B is a primary-key attribute and A is not a candidate key,
Whereas BCNF insists that for this dependency to remain in a relation, A must be a candidate key.
Example:
CLIENT INTERVIEW:
ClientNo
|
InterviewDate
|
InterviewTime
|
StaffNo
|
RoomNo
|
CR76
|
13-may-11
|
10:30
|
SG5
|
G101
|
CR76
|
13-may-11
|
12:00
|
SG5
|
G101
|
CR74
|
13-may-11
|
12:00
|
SG37
|
G102
|
CR56
|
02-july-11
|
10:30
|
SG5
|
G102
|
• FD1 ClientNo, InterviewDate -> InterviewTime, StaffNo, RoomNo (Primary Key)
• FD2 StaffNo, InterviewDate, InterviewTime -> ClientNo (Candidate key)
• FD3 RoomNo, InterviewDate, InterviewTime -> ClientNo, StaffNo (Candidate key)
• FD4 StaffNo, InterviewDate -> RoomNo (not a candidate key)
As a consequece the ClientInterview relation may suffer from update anomalies.
To transform the ClientInterview relation to BCNF, we must remove the violating functional dependency by creating two new relations called Interview and StaffRoom as shown below,
Interview (ClientNo, InterviewDate, InterviewTime, StaffNo)
StaffRoom (StaffNo, InterviewDate, RoomNo)
INTERVIEW
ClientNo
|
InterviewDate
|
InterviewTime
|
StaffNo
|
CR76
|
13-may-11
|
10:30
|
SG5
|
CR76
|
13-may-11
|
12:00
|
SG5
|
CR74
|
13-may-11
|
12:00
|
SG37
|
CR56
|
02-july-11
|
10:30
|
SG5
|
STAFFROOM
StaffNo
|
InterviewDate
|
RoomNo
|
SG5
|
13-may-11
|
G101
|
SG37
|
13-may-11
|
G102
|
SG5
|
02-july-11
|
G102
|
BCNF Interview and StaffRoom relations.
An entity is in Fourth Normal Form (4NF) when it meets the requirement of being in Third Normal Form (3NF) and additionally:
- Has no
multiple sets of multi-valued dependencies. In other words, 4NF states
that no entity can have more than a single one-to-many relationship within
an entity if the one-to-many attributes are independent of each other.
- Many:many
relationships are resolved independently.
Fourth Normal Form (4th NF)
In 4th NF:
An entity is in Fourth Normal Form (4NF) when it meets the requirement of being in Third Normal Form (3NF) and additionally:
- Has no
multiple sets of multi-valued dependencies. In other words, 4NF states
that no entity can have more than a single one-to-many relationship within
an entity if the one-to-many attributes are independent of each other.
- Fourth
Normal Form applies to situations involving many-to-many relationships.
In relational databases, many-to-many relationships are expressed through cross-reference tables.
Definition: A table is in fourth normal form (4NF) if and only if it is in BCNF and contains no more than one multi-valued dependency.
Example:
Take an example of Employee Table
info(Employee, Skills, Hobbies)
Employee
|
Skills
|
Hobbies
|
1
|
Programming
|
Golf
|
1
|
Programming
|
Bowling
|
1
|
Analysis
|
Golf
|
1
|
Analysis
|
Bowling
|
2
|
Analysis
|
Golf
|
2
|
Analysis
|
Gardening
|
2
|
Management
|
Golf
|
2
|
Management
|
Gardening
|
This table is difficult to maintain since adding a new hobby requires multiple new rows corresponding to each skill. This problem is created by the pair of multi-valued dependencies EMPLOYEE -> SKILLS and EMPLOYEE -> HOBBIES. A much better alternative would be to decompose INFO into two relations:
Employee
|
Skills
|
1
|
Programming
|
1
|
Analysis
|
2
|
Analysis
|
2
|
Management
|
Hobbies(Employee, Hobby)
Employee
|
Hobbies
|
1
|
Golf
|
1
|
Bowling
|
2
|
Golf
|
2
|
Gardening
|
Fifth Normal Form (5th NF)
In 5th NF:
- A
relation that has a join dependency cannot be decomposed by a projection
into other relations without spurious results
- A
relation is in 5NF when its information content cannot be reconstructed
from several smaller relations i.e. from relations having fewer attributes
than the original relation
Definition: A table is in fifth normal form (5NF) or Project-Join Normal Form (PJNF) if it is in 4NF and it cannot have a lossless decomposition into any number of smaller tables.
Fifth normal form, also known as join-projection normal form (JPNF), states that no non-trivial join dependencies exist. 5NF states that any fact should be able to be reconstructed without any anomalous results in any case, regardless of the number of tables being joined. A 5NF table should have only candidate keys and it's primary key should consist of only a single column.
Example:
Take an example of a buying table. This is used to track buyers, what they buy, and from whom they buy. Take the following sample data:
Buyer
|
Vendor
|
Item
|
Shalley
|
Kashmir House
|
Jeans
|
Mary
|
Kashmir House
|
Jeans
|
Shalley
|
Radhika Sarees
|
Saree
|
Mary
|
Radhika Sarees
|
Saree
|
Shalley
|
Radhika Sarees
|
Suit
|
The problem with the above table structure is that if Claiborne starts to sell Jeans then how many records must you create to record this fact? The problem is there are pair wise cyclical dependencies in the primary key. That is, in order to determine the item you must know the buyer and vendor, and to determine the vendor you must know the buyer and the item, and finally to know the buyer you must know the vendor and the item.
And the solution is to break this one table into three tables; Buyer-Vendor, Buyer-Item, and Vendor-Item. So following tables are in the 5NF.
BUYER-VENDOR
Buyer
|
Vendor
|
Shalley
|
Kashmir House
|
Mary
|
Kashmir House
|
Shalley
|
Radhika Sarees
|
Mary
|
Radhika Sarees
|
BUYER-ITEM
Buyer
|
Item
|
Shalley
|
Jeans
|
Mary
|
Jeans
|
Shalley
|
Saree
|
Mary
|
Saree
|
Shalley
|
Suit
|
VENDOR- ITEM
Vendor
|
Item
|
Kashmir House
|
Jeans
|
Radhika Sarees
|
Saree
|
Radhika Sarees
|
Suit
|
Subquery:-If a sql statement contains another sql statement then the sql statement which is inside another sql statement is called Subquery. It is also known as nested query. The Sql Statement which contains the other sql statement is called Parent Statement.
Nested Subquery:-If a Subquery contains another subquery, then the subquery inside another subquery is called nested subquery.
Correlated Subquery
A query is called correlated subquery when
both the inner query and the outer query are interdependent. For every row
processed by the inner query, the outer query is processed as well. The inner
query depends on the outer query before it can be processed.
Difference between CTE and Temp Table and Table Variable
Temp Table or
Table variable or CTE are commonly used for storing data temporarily in SQL
Server. In this article, you will learn the differences among these three.
CTE
CTE stands for Common Table
expressions. It was introduced with SQL Server 2005. It is a temporary result
set and typically it may be a result of complex sub-query. Unlike temporary
table its life is limited to the current query. It is defined by using WITH
statement. CTE improves readability and ease in maintenance of complex queries
and sub-queries. Always begin CTE with semicolon.
A sub query without
CTE is given below :
1.
SELECT * FROM (
2.
SELECT Addr.Address, Emp.Name,
Emp.Age From Address Addr
3.
Inner join Employee Emp on
Emp.EID = Addr.EID) Temp
4.
WHERE Temp.Age > 50
5.
ORDER BY Temp.NAME
By using CTE above
query can be re-written as follows :
1.
;With CTE1(Address, Name, Age)--Column names for CTE, which are optional
2.
AS
3.
(
4.
SELECT Addr.Address, Emp.Name, Emp.Age from Address Addr
5.
INNER JOIN EMP Emp ON Emp.EID = Addr.EID
6.
)
7.
SELECT * FROM CTE1 --Using CTE
8.
WHERE CTE1.Age > 50
9.
ORDER BY CTE1.NAME
When to use CTE
- This
is used to store result of a complex sub query for further use.
- This
is also used to create a recursive query.
Temporary Tables
In SQL Server, temporary tables are
created at run-time and you can do all the operations which you can do on a
normal table. These tables are created inside Tempdb database. Based on the
scope and behavior temporary tables are of two types as given below-
- Local Temp Table
Local temp
tables are only available to the SQL Server session or connection (means single
user) that created the tables. These are automatically deleted when the session
that created the tables has been closed. Local temporary table name is stared
with single hash ("#") sign.
1.
CREATE TABLE #LocalTemp
2.
(
3.
UserID int,
4.
Name varchar(50),
5.
Address varchar(150)
6.
)
7.
GO
8.
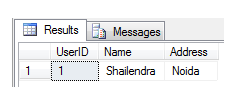
insert into #LocalTemp values ( 1, 'Shailendra','Noida');
9.
GO
The scope
of Local temp table exist to the current session of current user means to the
current query window. If you will close the current query window or open a new
query window and will try to find above created temp table, it will give you
the error.
- Global Temp Table
Global temp
tables are available to all SQL Server sessions or connections (means all the
user). These can be created by any SQL Server connection user and these are
automatically deleted when all the SQL Server connections have been closed.
Global temporary table name is stared with double hash ("##") sign.
1.
CREATE TABLE ##GlobalTemp
2.
(
3.
UserID int,
4.
Name varchar(50),
5.
Address varchar(150)
6.
)
7.
GO
8.
insert into ##GlobalTemp values ( 1, 'Shailendra','Noida');
9.
GO
10.
Select * from ##GlobalTemp
Global
temporary tables are visible to all SQL Server connections while Local
temporary tables are visible to only current SQL Server connection.
Table Variable
This acts like a variable and exists
for a particular batch of query execution. It gets dropped once it comes out of
batch. This is also created in the Tempdb database but not the memory. This
also allows you to create primary key, identity at the time of Table variable
declaration but not non-clustered index.
1.
GO
2.
DECLARE @TProduct TABLE
3.
(
4.
SNo INT IDENTITY(1,1),
5.
ProductID INT,
6.
Qty INT
7.
)
8.
--Insert data to Table variable
@Product
9.
INSERT INTO
@TProduct(ProductID,Qty)
10.
SELECT DISTINCT ProductID, Qty
FROM ProductsSales ORDER BY ProductID ASC
11.
--Select data
12.
Select * from @TProduct
13.
14.
--Next batch
15.
GO
16.
Select * from @TProduct --gives
error in next batch
17.
Note
- Temp
Tables are physically created in the Tempdb database. These tables act as
the normal table and also can have constraints, index like normal tables.
- CTE is
a named temporary result set which is used to manipulate the complex
sub-queries data. This exists for the scope of statement. This is created
in memory rather than Tempdb database. You cannot create any index on CTE.
- Table
Variable acts like a variable and exists for a particular batch of query
execution. It gets dropped once it comes out of batch. This is also
created in the Tempdb database but not the memory.
In subqueries, which is efficient
,the IN clause or EXISTS clause? Does they produce the same result?????
EXISTS is efficient bcose,
1.Exists is faster than IN clause.
2.IN check returns values to main query where as EXISTS returns Boolean (T or F).
1.Exists is faster than IN clause.
2.IN check returns values to main query where as EXISTS returns Boolean (T or F).
In terms of optimization both are different,Exists is used where both the
queries(main and subqueries) returns the same structure results like select
name,id from emp where exists (select depname,depid from dep)but if the
returning structure is different then we use In clause for exp select name,id
from emp where id in(select depid from dep
)
)
A transaction is a unit of work that is
performed against a database. Transactions are units or sequences of work
accomplished in a logical order, whether in a manual fashion by a user or
automatically by some sort of a database program.
A transaction is the propagation of one
or more changes to the database. For example, if you are creating a record or
updating a record or deleting a record from the table, then you are performing
transaction on the table. It is important to control transactions to ensure
data integrity and to handle database errors.
Practically, you will club many SQL
queries into a group and you will execute all of them together as a part of a
transaction.
Properties of
Transactions:
Transactions have the following four
standard properties, usually referred to by the acronym ACID:
- Atomicity: ensures that all operations within the work unit are completed
successfully; otherwise, the transaction is aborted at the point of
failure, and previous operations are rolled back to their former state.
- Consistency: ensures that the database properly changes states upon a
successfully committed transaction.
- Isolation: enables transactions to operate independently of and transparent
to each other.
- Durability: ensures that the result or effect of a committed transaction persists
in case of a system failure.
what is computed column in sql server:-
Computed columns are derived columns based on the
other existing columns. Computed columns are a data type that can be created
based on the situation.
We can create a computed column at either of the following two levels:
We can create a computed column at either of the following two levels:
- Whenever we create the table.
- By using an alter statement.
What is denormalization and when would you go for it?
De-normalization is the process of attempting to optimize the performance of a database by adding redundant data. It’s used To introduce redundancy into a table in order to incorporate data from a related table. The related table can then be eliminated. De-normalization can improve efficiency and performance by reducing complexity in a data warehouse schema.
The Reason for Denormalization
Only one valid reason exists for denormalizing a relational design - to enhance performance. However, there are several indicators which will help to identify systems and tables which are potential denormalization candidates. These are:
• Many critical queries and reports exist which rely upon data from more than one table. Often times these requests need to be processed in an on-line environment.
• Repeating groups exist which need to be processed in a group instead of individually.
• Many calculations need to be applied to one or many columns before queries can be successfully answered.
• Tables need to be accessed in different ways by different users during the same timeframe.
• Many large primary keys exist which are clumsy to query and consume a large amount of disk space when carried as foreign key columns in related tables.
• Certain columns are queried a large percentage of the time causing very complex or inefficient SQL to be used.
What is
view ?Advantages and Disadvantages of
views in Sql Server
What is view ?
View is the simply
subset of table which are stored logically in a database means
a view is a virtual table in the database whose contents are defined by a
query.
To the database
user, the view appears just like a real table, with a set of named columns and
rows of data. SQL creates the illusion of the view by giving the view a name
like a table name and storing the definition of the view in the database.
Views are used for
security purpose in databases,views restricts the user from viewing
certain column and rows means by using view we can apply the restriction on
accessing the particular rows and columns for specific user. Views display only
those data which are mentioned in the query, so it shows only data which is
returned by the query that is defined at the time of creation of the
View.
Advantages of views
Security
Each user can be given
permission to access the database only through a small set of views that
contain the specific data the user is authorized to see, thus restricting the
user's access to stored data
Query Simplicity
A view can draw
data from several different tables and present it as a single table, turning
multi-table queries into single-table queries against the view.
Structural
simplicity
Views can give a
user a "personalized" view of the database structure, presenting the
database as a set of virtual tables that make sense for that user.
Consistency
A view can present
a consistent, unchanged image of the structure of the database, even if the
underlying source tables are split, restructured, or renamed.
Data Integrity
If data is accessed
and entered through a view, the DBMS can automatically check the data to ensure
that it meets the specified integrity constraints.
Logical data
independence.
View can make
the application and database tables to a certain extent independent. If there
is no view, the application must be based on a table. With the view, the
program can be established in view of above, to view the program with a
database table to be separated.
Disadvantages of
views
Performance
Views create the
appearance of a table, but the DBMS must still translate queries against the
view into queries against the underlying source tables. If the view is defined
by a complex, multi-table query then simple queries on the views may take
considerable time.
Update restrictions
When a user tries
to update rows of a view, the DBMS must translate the request into an update on
rows of the underlying source tables. This is possible for simple views, but
more complex views are often restricted to read-only.
What is Linked Servers or
Database Links?How to setup Linked Servers?
Don't be
confused by the two terms; both are the same. In SQL Server it is called a
Linked Server whereas in Oracle it's DBLinks (Database Links).
Linked Servers
allows you to connect to other database instances on the same server or on
another machine or remote servers.
It allows SQL
Server to execute SQL scripts against OLE DB data sources on remote servers
using OLE DB providers.
The remote servers
can be SQL Server, Oracle etc. which means those databases tht support OLE DB
can be used for linking servers.
How to setup Linked Servers?
Referer:http://www.c-sharpcorner.com/uploadfile/suthish_nair/linked-servers-in-sql-server-2008/
This can be done in
two ways.
1.Using Transact-SQL
2.SQL Server Management Studio
Handling error in sql server?
The two most common mechanisms for error handling
in SQL Server 2005 are:
- @@ERROR
- TRY-CATCH Block
How we find third, Fourth and Fifth highest salary through SQl queries?
2nd Highest Salaryselect max(salary) from Employeedetails
where salary not in (select top 1 salary from Employeedetails order by salary desc )
3nd Highest Salary
select max(salary) from Employeedetails
where salary not in (select top 2 salary from Employeedetails order by salary desc )
4nd Highest Salary
select max(salary) from Employeedetails
where salary not in (select top 3 salary from Employeedetails order by salary desc )
...................